在当今容器化部署的世界中,高效构建和部署后端应用程序至关重要。 fastapi 已成为创建快速、高性能 api 的最流行的 框架之一。为了管理依赖关系,我们还可以利用 uv(包管理器)作为一个方便的工具。
紫外线
我假设您之前已经在本地安装了 uv 和 。
现在,我们可以通过使用以下命令初始化我们的项目来继续创建我们的应用程序: uv init simple-app
uv 将创建以下文件:
simple-app/ ├── .python-version ├── readme.md ├── hello.py └── pyproject.toml
pyproject.toml 文件包含有关我们项目的元数据:
[project] name = "simple-app" version = "0.1.0" description = "add your description here" readme = "readme.md" requires-python = ">=3.11" dependencies = []
接下来,我们可以开始添加项目依赖项。您最终应该在 pyproject.toml 中得到以下结构:
dependencies = [ "fastapi[standard]<1.0.0,>=0.114.2", "python-multipart<1.0.0,>=0.0.7", "email-validator<3.0.0,>=2.1.0", "pydantic>2.0", "sqlalchemy>2.0", "alembic<2.0.0,>=1.12.1", ] [tool.uv] dev-dependencies = [ "pytest<8.0.0,>=7.4.3", "mypy<2.0.0,>=1.8.0", "ruff<1.0.0,>=0.2.2", "pre-commit<4.1.0,>=4.0.0", ]
注意 [tool.uv] 部分:在这里,我们定义了一些在部署项目时将排除的依赖项,因为在该阶段不需要它们。
此时,我们还没有创建任何虚拟环境。为此,只需运行:uvsync,uv 将执行以下操作
立即学习“”;
- 创建 uv.lock 文件。
- 使用指定的python版本(如pyproject.toml中的.python-version和requires-python所示)创建虚拟环境(.venv文件夹)。如果 uv 找不到本地 python 解释器,它将下载一个。
- 安装所有依赖项。
快速api
现在,我们可以通过添加以下文件夹结构来开始手动创建 fastapi 应用程序:
recipe-app/ ├── app/ │ ├── main.py │ ├── __init__.py │ └── ... ├── .python-version ├── readme.md └── pyproject.toml
在mn.py中,添加以下代码:
from fastapi import fastapi from pydantic import basemodel app = fastapi() class hello(basemodel): message: str @app.get("/", response_model=hello) async def hello() -> hello: return hello(message="hi, i am using fastapi")
我们可以通过执行以下命令来运行我们的项目:uv run fastapi dev app/main.py,您应该看到类似于以下内容的输出
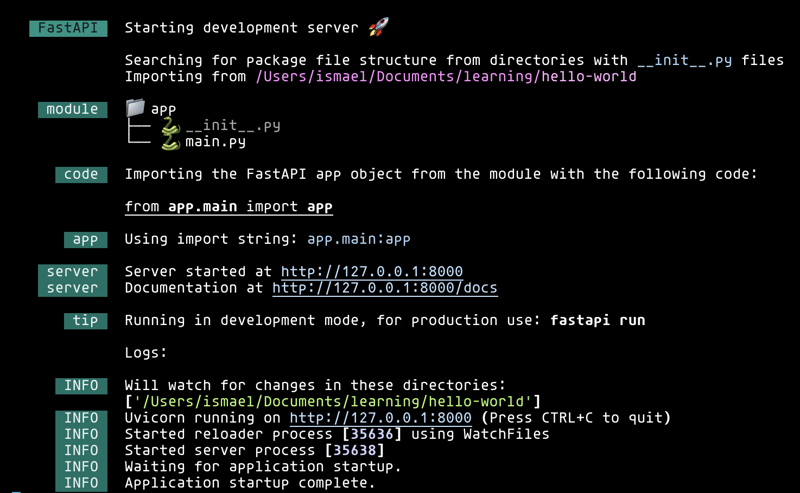
如果您转到http://127.0.0.1:8000/,,您将看到:消息“嗨,我正在使用 fastapi”
码头工人
到目前为止,一切都很好。但是,我们还没有集成 docker。我们将使用容器进行开发(有人认为这不方便,但这最终取决于您)。另外,我们将在容器内使用 uv,这可能是有争议的,但这是我习惯的。
uv 在这里提供了一些有关在 docker 中使用 uv 的有用信息。我们首先使用以下配置在应用程序的根目录添加 dockerfile:
from python:3.11-slim env pythonunbuffered=1 copy --from=ghcr.io/astral-sh/uv:0.5.11 /uv /uvx /bin/ env uv_compile_byte=1 env uv_link_mode=copy # change the working directory to the `app` directory workdir /app env path="/app/.venv/bin:$path" copy ./pyproject.toml ./uv.lock ./.python-version /app/ # install dependencies run --mount=type=cache,target=/root/.cache/uv --mount=type=bind,source=uv.lock,target=uv.lock --mount=type=bind,source=pyproject.toml,target=pyproject.toml uv sync --frozen --no-install-project --no-dev # copy the project into the image copy ./app /app/app # sync the project run --mount=type=cache,target=/root/.cache/uv uv sync --frozen --no-dev cmd ["fastapi", "dev", "app/main.py", "--host", "0.0.0.0"]
虽然您可以创建多阶段 dockerfile,但我们在本教程中让事情变得更简单。
我们可以只使用我们的容器,但是我发现创建一个 docker-compose.yaml 文件来管理我们所有的容器更方便:
services: app: # build configuration for the "app" service: # - 'context: .' tells docker to use the current directory as the build context # - 'dockerfile: dockerfile' specifies the file to use for building the image build: context: . dockerfile: dockerfile # this sets the default working directory inside the container working_dir: /app # mounts the local "app" directory into the container so code changes are reflected without rebuild volumes: - ./app:/app/app # maps the container port 8000 to the host machine port defined by app_port # if app_port is not set, it defaults to 8000 ports: - "${app_port:-8000}:8000" # passes the database_url environment variable to the container environment: - database_url=${database_url} # ensures the 'app' service won't start until 'postgres' is running depends_on: - postgres postgres: ## just for reference... # official postgres image version 15 image: postgres:15 # set up the default database, user, and password environment: postgres_db: ${postgres_db} postgres_user: ${postgres_user} postgres_password: ${postgres_password} # this volume stores postgresql data outside of the container filesystem, # preserving data between container restarts or recreations volumes: - postgres_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data # declare named volumes to be used for persistent storage volumes: postgres_data: {}
要运行所有容器,请创建一个包含所有必需变量的 .env 文件。
您可能想知道我们需要两次定义数据库凭据。嗯,database_url 用于 alembic 和 sqlalchemy,各个凭据用于数据库本身。这看似重复,但我们只需要配置一次。
一切设置完毕后,我们可以使用以下命令运行我们的项目: docker compose up –build
[工具.uv]
我们需要介绍的最后一部分是 pyproject.toml 中的 [tool.uv] 部分,我们在其中列出了开发依赖项。
-
pytest
- pytest 是 python 中广泛使用的测试框架,允许您编写小型、简洁的测试,同时提供强大的功能,例如固定装置和断言。
-
mypy
- mypy 是 python 的静态类型检查器,它使用类型提示 (pep 484) 在运行前检测潜在的错误或不一致。
-
皱褶
- ruff 是一个快速的 python linter,用 rust 编写,能够通过提供彻底的样式、错误和格式检查来替换多个工具(例如 flake8、isort)。
-
预提交
- 预提交是一个用于管理和维护多语言预提交挂钩的框架,通过在提交最终确定之前运行检查来确保代码库的一致性和质量。
由于 pytest 超出了范围,我们将首先配置 ruff 并预提交。我们需要创建一个 .pre-commit-config.yaml 文件,每次执行 提交操作时都会运行该文件。以下是建议的配置:
repos: - repo: https://github.com/pre-commit/pre-commit-hooks rev: v4.4.0 hooks: - id: check-added-large-files - id: check-toml - id: check-yaml args: - --unsafe - id: end-of-file-fixer - id: trailing-whitespace - repo: https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-pre-commit rev: v0.8.6 hooks: - id: ruff args: [--fix] - id: ruff-format
您也可以在预提交中配置 mypy,但这可能有点棘手,因为它需要一个隔离的环境来检查您的代码,并且可能无法找到已经属于您的依赖项的包。这就是为什么我更喜欢通过执行以下命令来手动运行它: uv run mypy app 它将在我们的应用程序文件夹上运行 mypy。
可以为 mypy 和 ruff 添加额外的配置到 pyproject.toml 中。这是我的标准配置(有些值是默认值,但我更喜欢明确):
[tool.mypy] strict = true exclude = ["venv", ".venv", "alembic"] ignore_missing_imports = true allow_untyped_decorators = true plugins = ["pydantic.mypy"] follow_imports = "silent" warn_redundant_casts = true warn_unused_ignores = true disallow_any_generics = true no_implicit_reexport = true disallow_untyped_defs = true [tool.pydantic-mypy] init_forbid_extra = true init_typed = true warn_required_dynamic_aliases = true [tool.ruff] target-version = "py312" exclude = ["venv", ".venv", "alembic"] line-length = 100 indent-width = 4 [tool.ruff.lint] select = [ "E", # pycodestyle errors "W", # pycodestyle warnings "F", # pyflakes "I", # isort "B", # flake8-bugbear "C4", # flake8-comprehensions "UP", # pyupgrade "ARG001", # unused arguments in functions ] ignore = [ "B008", # do not perform function calls in argument defaults "W191", # indentation contains tabs "B904", # Allow raising exceptions without from e, for HTTPException ] [tool.ruff.format] quote-style = "double" line-ending = "auto" [tool.ruff.lint.pyupgrade] # Preserve types, even if a file imports `from __future__ import annotations`. keep-runtime-typing = true [tool.pyright] ignore = ["alembic"]
现在您可以直接从 vs code marketplace 安装 ruff 扩展。该插件将自动检查您的代码并实时突出显示问题,在您工作时提供即时反馈,该扩展将考虑 pyproject.toml
中的所有配置
通过此配置,您的开发环境将强制执行一致的代码风格、类型检查和预提交检查,从而为使用 uv 构建容器化 fastapi 应用程序提供更顺畅的工作流程。
以上就是可扩展的 Python 后端:使用 uv、Docker 和预提交构建容器化 FastAPI 应用程序:分步指南的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!
 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏
 支付宝扫一扫打赏
支付宝扫一扫打赏

